How to Tell Tombstone PCB Defects ‘Rest in Peace’
Working with small circuit board areas can increase the risk of various PCB defects, tombstoning in particular. While the grim nature of “tombstone”...
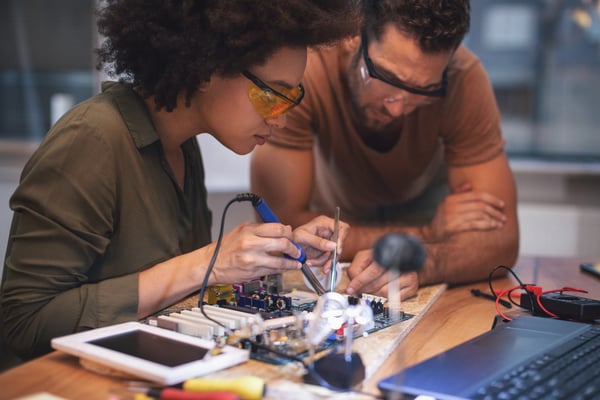

Let’s face it, soldering can be a challenging task. Even with years of training and the most advanced machinery, PCB soldering defects are sometimes unavoidable. At one point or another, you’ll likely encounter an issue that threatens to derail your project's timeline and budget.
Understanding the most common soldering defects and the steps you can take to avoid them is the first step toward preventing PCB failure.
This guide covers the most common types of PCB soldering defects to help you minimize headaches and prevent defective batches.
Soldering defects can occur for various reasons, ranging from operator error to environmental pollutants. Understanding how to identify these well-known, and often frustrating, defects is important for anyone involved in PCB design, manufacturing, and quality control.
An open solder joint is a common PCB defect where there is no proper connection between a component's lead and the corresponding pad on the circuit board. This typically happens when the solder fails to bond to both surfaces, often leaving the solder only on the PCB but not on the component lead.
The result is an open circuit, rendering that part of the board non-functional.
Applying too much solder can create large bubbles or balls at the joint. While the joint might still be functional, these solder balls can hide other mistakes, such as poor wetting or even a solder bridge in disguise.
Excessive solder also adds unnecessary weight and can make future repairs or inspections more difficult.
A component shift occurs when a part becomes misaligned on its target pads. This often happens during the reflow process when parts float on the molten solder and settle in the wrong position as the solder cools.
This misalignment can lead to open circuits or short circuits, causing immediate PCB failure. This is one of the reasons that services like flying probe testing are so valuable for quality assurance.
When the soldering iron is at too low a temperature or the joint isn't heated long enough, a cold joint can form. These joints have a rough, messy appearance and are structurally weak. They create an unreliable electrical connection that can fail over time, limiting the functionality of the PCB.
Proper soldering techniques and certifications like IPC J-STD-001 are essential for avoiding this issue.
A solder bridge is a tiny, often hard-to-see connection of solder that improperly links one lead to another. This unintended connection creates a short circuit, which can cause significant damage.
A solder bridge can burn up components, blow a trace on the PCB, or lead to a complete board failure.
Webbing and splashing are types of PCB solder mask defects that occur when pollutants or moisture on the board's surface disrupt the soldering process. This results in thin, web-like strands of solder or scattered splashes across the board.
While they may seem like cosmetic issues, they pose a serious short-circuit hazard and can compromise the board's reliability.
A lifted pad happens when a pad detaches from the surface of the circuit board. While not always a direct soldering defect, it can be caused by excessive force on a joint that has insufficient solder. A lifted pad can easily cause a short circuit, potentially damaging or destroying the board.
Understanding this type of failure is critical to passing any solderability test standard.
Experiencing these defects, while frustrating, provides valuable learning opportunities for any electronics pro. For companies dealing with the challenges of product life cycle management for medical devices, minimizing these failures is critical.
If you are consistently running into PCB soldering defects, it may be time to consult an expert. An American PCB manufacturer partner can provide a thorough printed circuit board failure analysis and help you navigate design, assembly, and aftermarket challenges.
(Editor's note: This blog was originally published in July 2020 and was updated in October 2025 with the most current information.)

Working with small circuit board areas can increase the risk of various PCB defects, tombstoning in particular. While the grim nature of “tombstone”...

There are many areas in life where accepting mistakes as inevitable is a good thing -- electronics manufacturing is not one of them. The end goal...
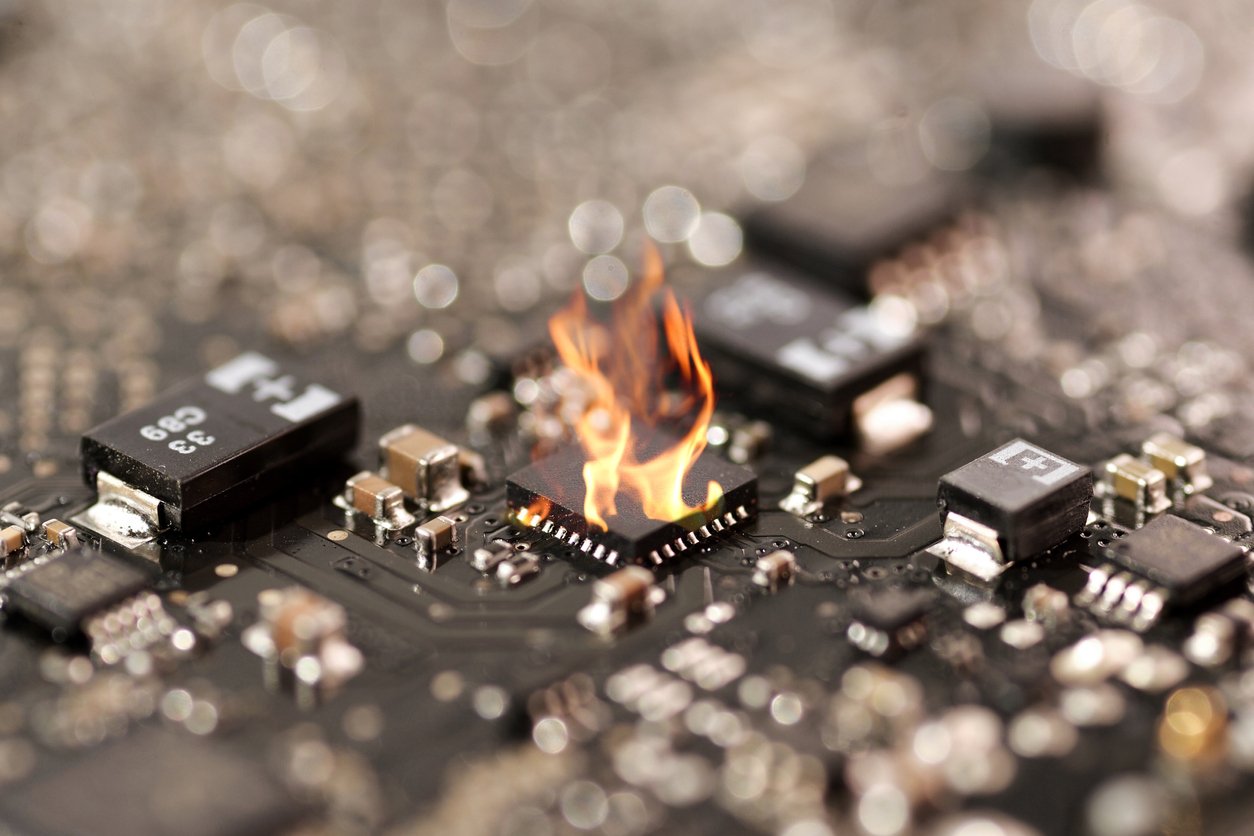
While there are many common printed circuit board defects, one of the most notorious is burnt components. It's also, unfortunately, one of the most...