Financial PCBs 101: Server PCBs in the Infrastructure
PCBs are crucial to modern financial systems and play a critical role in the infrastructure that supports the global financial ecosystem. These...
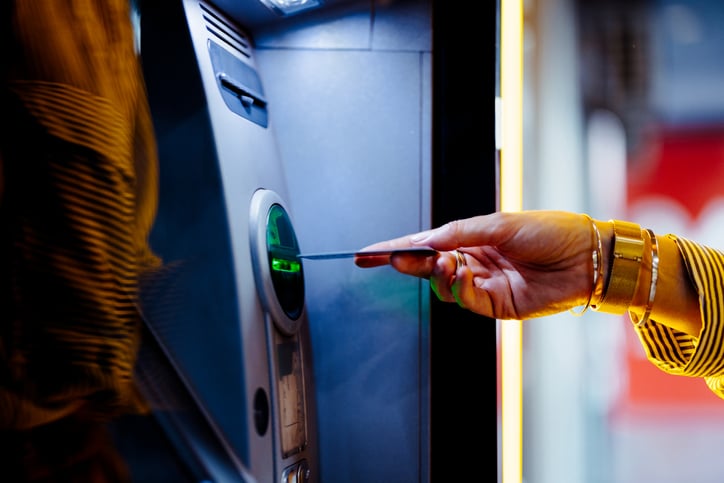

PCBs for kiosks represent a specialized area within electronics manufacturing, requiring a focus on durability, security, and diverse component integration. As technology advances, the role of PCBs in kiosks will continue to grow, supporting more complex applications and enhancing user experiences.
Today's technology landscape is increasingly dominated by the Internet of Things (IoT), a network of interconnected devices that communicate and exchange data with each other and with centralized systems over the Internet. This technological evolution has paved the way for advanced service delivery mechanisms across various sectors, including the financial industry. Financial kiosks are a prime example of how diverse technologies converge to offer complex services in a user-friendly and accessible manner.
Financial kiosks, such as ATMs, information kiosks, and self-service banking terminals, embody the integration of multiple technologies to deliver a wide range of financial services. These kiosks leverage IoT technology for real-time connectivity, allowing them to perform tasks like updating account information, processing transactions, and providing personalized financial advice based on data analysis.
 Financial kiosks are sophisticated machines that incorporate a wide array of technological components designed to facilitate financial transactions and services. At their core, these kiosks integrate high-performance computing systems powered by advanced PCBs (Printed Circuit Boards) that manage data processing and user interactions.
Financial kiosks are sophisticated machines that incorporate a wide array of technological components designed to facilitate financial transactions and services. At their core, these kiosks integrate high-performance computing systems powered by advanced PCBs (Printed Circuit Boards) that manage data processing and user interactions.
Connectivity is another critical component, with financial kiosks requiring robust network interfaces (both wired and wireless) to connect securely to banking servers and process transactions in real-time.
Each of these components is designed with security, durability, and reliability in mind, ensuring that financial kiosks can serve the public efficiently and securely Below we outline four main components that work together to provide a satisfactory user experience to the public:
Financial kiosks are designed to offer a range of services, from cash withdrawals and deposits to account management and financial advice. The combination of IoT connectivity, robust hardware, advanced software, and stringent security measures allows these kiosks to deliver these services reliably and securely. They can adapt to user preferences, provide services tailored to individual needs, and even predict future financial trends for their users.
Moreover, the data collected from these kiosks, when analyzed, can offer insights into consumer behavior, helping financial institutions refine their services and introduce new products tailored to the needs of their customers.
In essence, financial kiosks are at the forefront of applying today's technology to create highly accessible, efficient, and secure financial services. They exemplify how the convergence of various technologies, orchestrated through the principles of IoT, can deliver specific and complex services that cater to the evolving needs of consumers.
The design and reliability of Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are foundational to the functionality and longevity of modern electronic devices, especially in applications within the Internet of Things (IoT), where devices are interconnected to perform complex tasks. Three critical considerations in PCB design for several reasons:
 PCBs must withstand various environmental stresses, including temperature variations, humidity, and physical shocks. This is particularly crucial for devices used in outdoor or industrial settings, where conditions can be harsh.
PCBs must withstand various environmental stresses, including temperature variations, humidity, and physical shocks. This is particularly crucial for devices used in outdoor or industrial settings, where conditions can be harsh.
Durable PCBs also ensure the long-term reliability of the devices they power, reducing the need for frequent replacements and maintenance. This is essential for consumer electronics, automotive applications, and industrial machinery, where failure can have significant consequences.
By carefully selecting materials and implementing thoughtful design considerations, the durability of PCBs is enhanced, leading to more reliable and longer-lasting electronic devices. These strategies must be tailored to the specific requirements and constraints of each application to achieve the best results. SMT technology, component placement, and the use of protective coatings are only some of the material considerations that are involved in successful PCB design.
As IoT devices often collect and transmit sensitive information, PCBs must incorporate security measures to protect against unauthorized access and data breaches. This is especially important in applications like financial kiosks, smart home devices, and healthcare monitors.
Implementing hardware-based security features on PCBs, such as cryptographic chips and secure boot mechanisms, can provide robust protection against tampering and cyber threats. Also, adhering to security standards and protocols during PCB design ensures that the devices meet industry-specific security requirements, which is critical for consumer trust and regulatory approval.
PCBs must support a wide range of connectivity options (e.g., Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, NFC, LTE) to enable seamless communication within the IoT ecosystem. This allows devices to connect to networks, communicate with other devices, and transfer data efficiently.
Ensuring stable and reliable connections is vital for the seamless operation of IoT devices. PCB design must account for signal integrity, minimizing interference, and optimizing antenna placement for wireless connections.
For many IoT devices, especially those that are battery-powered, maintaining connectivity with minimal energy consumption is crucial. PCBs need to be designed with power management features that optimize energy use without compromising performance.
The integration of durability, security, and connectivity into PCB design not only addresses the functional requirements of modern electronic devices but also ensures their reliability and longevity in the field. As technology evolves, the importance of these aspects will only increase, pushing the boundaries of PCB design and manufacturing techniques further.
For more on the PCB assembly process, dive into these resources from our blog library:
The importance of durability, security, and connectivity in PCB design cannot be overstated. These elements are critical to the performance, reliability, and user trust in the vast array of electronic devices that populate our modern, interconnected world.
Whether it's for consumer electronics, automotive systems, industrial applications, or IoT devices, PCBs must be meticulously designed to meet these stringent requirements, ensuring that they can deliver the specific, complex services expected of them securely and reliably.

PCBs are crucial to modern financial systems and play a critical role in the infrastructure that supports the global financial ecosystem. These...
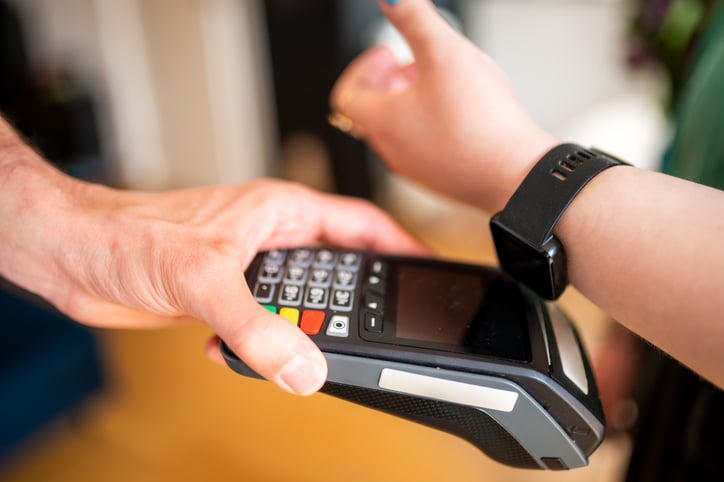

In the digital age, where transactions are often completed with a mere tap or click, the seamless operation of financial systems has become a...

Data centers are crucial for the financial industry due to their pivotal role in ensuring speed, reliability, and security, which are fundamental for...